The blog post was originally published on my Czech blog.
When we launched Vhsky.cz a year ago, we did it to provide an alternative to the near-monopoly of YouTube. I believe video distribution is so important today that it’s a skill we should maintain ourselves.
To be honest, it’s bothered me for the past few years that even open-source conferences simply rely on YouTube for streaming talks, without attempting to secure a more open path. We are a community of tech enthusiasts who tinker with everything and take pride in managing things ourselves, yet we just dump our videos onto YouTube, even when we have the tools to handle it internally. Meanwhile, it’s common for conferences abroad to manage this themselves. Just look at FOSDEM or Chaos Communication Congress.
This is why, from the moment Vhsky.cz launched, my ambition was to broadcast talks from OpenAlt—a conference I care about and help organize. The first small step was uploading videos from previous years. Throughout the year, we experimented with streaming from OpenAlt meetups. We found that it worked, but a single stream isn’t quite the stress test needed to prove we could handle broadcasting an entire conference.
For several years, Michal Vašíček has been in charge of recording at OpenAlt, and he has managed to create a system where he handles recording from all rooms almost single-handedly (with assistance from session chairs in each room). All credit to him, because other conferences with a similar scope of recordings have entire teams for this. However, I don’t have insight into this part of the process, so I won’t focus on it. Michal’s job was to get the streams to our server; our job was to get them to the viewers.

Stress Test
We only got to a real stress test the weekend before the conference, when Bashy prepared a setup with seven streams at 1440p resolution. This was exactly what awaited us at OpenAlt. Vhsky.cz runs on a fairly powerful server with a 32-core i9-13900 processor and 96 GB of RAM. However, it’s not entirely dedicated to PeerTube. It has to share the server with other OSCloud services (OSCloud is a community hosting of open source web services).
We hadn’t been limited by performance until then, but seven 1440p streams were truly at the edge of the server’s capabilities, and streams occasionally dropped. In reality, this meant 14 continuous transcoding processes, as we were streaming in both 1440p and 480p. Even if you don’t change the resolution, you still need to transcode the video to leverage useful distribution features, which I’ll cover later. The 480p resolution was intended for mobile devices and slow connections.
Remote Runner
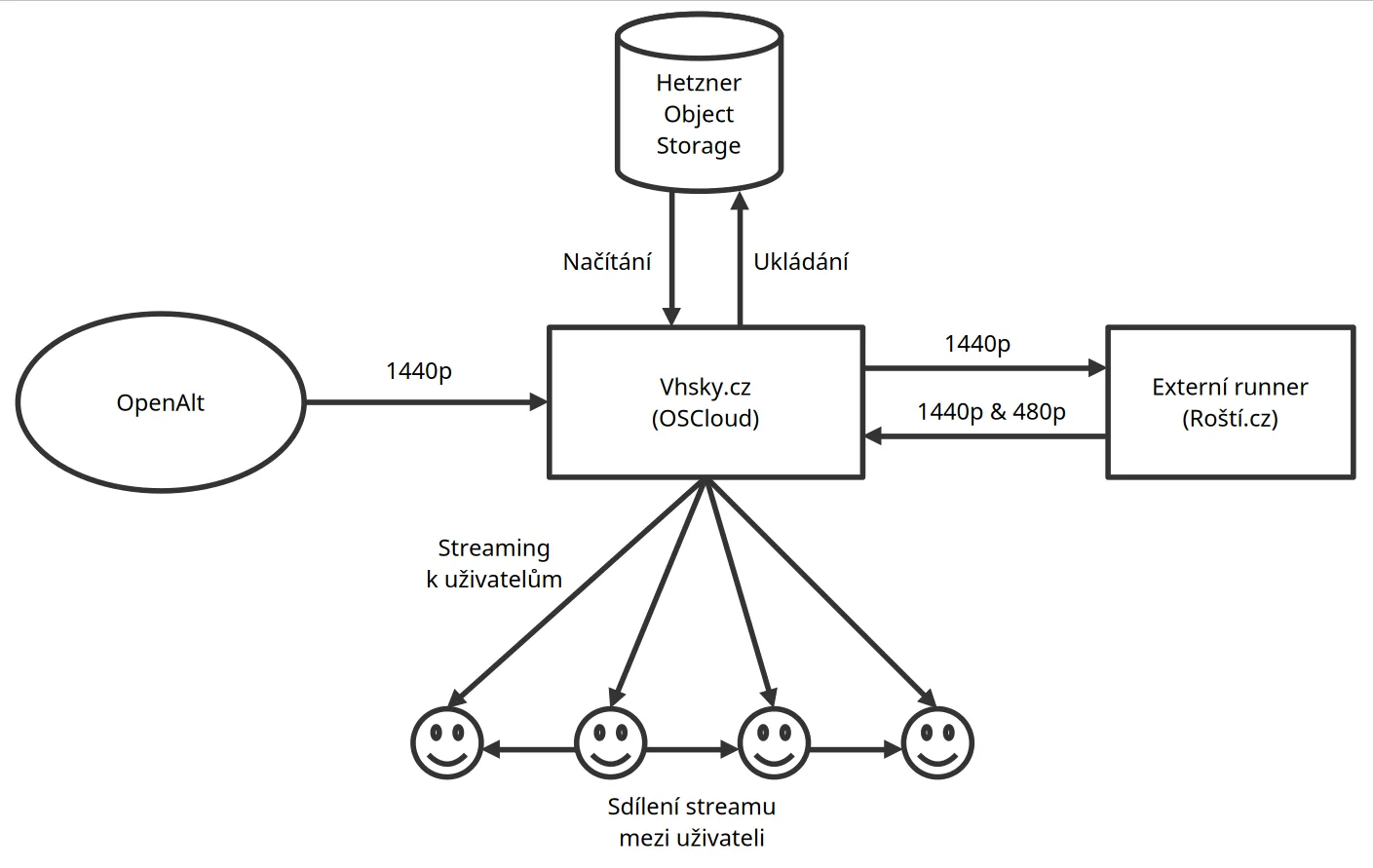
We knew the Vhsky.cz server alone couldn’t handle it. Fortunately, PeerTube allows for the use of “remote runners”. The PeerTube instance sends video to these runners for transcoding, while the main instance focuses only on distributing tasks, storage, and video distribution to users. However, it’s not possible to do some tasks locally and offload others. If you switch transcoding to remote runners, they must handle all the transcoding. Therefore, we had to find enough performance somewhere to cover everything.
I reached out to several hosting providers known to be friendly to open-source activities. Adam Štrauch from Roští.cz replied almost immediately, saying they had a backup machine that they had filed a warranty claim for over the summer and hadn’t tested under load yet. I wrote back that if they wanted to see how it behaved under load, now was a great opportunity. And so we made a deal.
It was a truly powerful machine: a 48-core Ryzen with 1 TB of RAM. Nothing else was running on it, so we could use all its performance for video transcoding. After installing the runner on it, we passed the stress test. As it turned out, the server with the runner still had a large reserve. For a moment, I toyed with the idea of adding another resolution to transcode the videos into, but then I decided we’d better not tempt fate. The stress test showed us we could keep up with transcoding, but not how it would behave with all the viewers. The performance reserve could come in handy.
Smart Video Distribution
Once we solved the transcoding performance, it was time to look at how PeerTube would handle video distribution. Vhsky.cz has a bandwidth of 1 Gbps, which isn’t much for such a service. If we served everyone the 1440p stream, we could serve a maximum of 100 viewers. Fortunately, another excellent PeerTube feature helps with this: support for P2P sharing using HLS and WebRTC.
Thanks to this, every viewer (unless they are on a mobile device and data) also becomes a peer and shares the stream with others. The more viewers watch the stream, the more they share the video among themselves, and the server load doesn’t grow at the same rate.
A two-year-old stress test conducted by the PeerTube developers themselves gave us some idea of what Vhsky could handle. They created a farm of 1,000 browsers, simulating 1,000 viewers watching the same stream or VOD. Even though they used a relatively low-performance server (quad-core i7-8700 CPU @ 3.20GHz, slow hard drive, 4 GB RAM, 1 Gbps connection), they managed to serve 1,000 viewers, primarily thanks to data sharing between them. For VOD, this saved up to 98% of the server’s bandwidth; for a live stream, it was 75%:

If we achieved a similar ratio, then even after subtracting 200 Mbps for overhead (running other services, receiving streams, data exchange with the runner), we could serve over 300 viewers at 1440p and multiples of that at 480p. Considering that OpenAlt had about 160 online viewers in total last year, this was a more than sufficient reserve.
Live Operation
On Saturday, Michal fired up the streams and started sending video to Vhsky.cz via RTMP. And it worked. The streams ran smoothly and without stuttering. In the end, we had a maximum of tens of online viewers at any one time this year, which posed no problem from a distribution perspective.

Our solution, which PeerTube allowed us to flexibly assemble from servers in different data centers, has one disadvantage: it creates some latency. In our case, however, this meant the stream on Vhsky.cz was about 5-10 seconds behind the stream on YouTube, which I don’t think is a problem. After all, we’re not broadcasting a sports event.
Minor Problems
We did, however, run into minor problems and gained experience that one can only get through practice. During Saturday, for example, we found that the stream would occasionally drop from 1440p to 480p, even though the throughput should have been sufficient. This was because the player felt that the delivery of stream chunks was delayed and preemptively switched to a lower resolution. Setting a higher cache increased the stream delay slightly, but it significantly reduced the switching to the lower resolution.
Subjectively, even 480p wasn’t a problem. Most of the screen was taken up by the red frame with the OpenAlt logo and the slides. The speaker was only in a small window. The reduced resolution only caused slight blurring of the text on the slides, which I wouldn’t even have noticed as a problem if I wasn’t focusing on it. I could imagine streaming only in 480p if necessary. But it’s clear that expectations regarding resolution are different today, so we stream in 1440p when we can.
Over the whole weekend, the stream from one room dropped for about two talks. For some rooms, viewers complained that the stream was too quiet, but that was an input problem. This issue was later fixed in the recordings.
When uploading the talks as VOD (Video on Demand), we ran into the fact that PeerTube itself doesn’t support bulk uploads. However, tools exist for this, and we’d like to use them next time to make uploading faster and more convenient. Some videos also uploaded with the wrong orientation, which was likely a problem in their metadata, as PeerTube wasn’t the only player that displayed them that way. YouTube, however, managed to handle it. Re-encoding them solved the problem.
On Saturday, to save performance, we also tried transcoding the first finished talk videos on the external runner. For these, a bar is displayed with a message that the video failed to save to external storage, even though it is clearly stored in object storage. In the end we had to reupload them because they were available to watch, but not indexed.
A small interlude – my talk about PeerTube at this year’s OpenAlt. Streamed, of course, via PeerTube:
Thanks and Support
I think that for our very first time doing this, it turned out very well, and I’m glad we showed that the community can stream such a conference using its own resources. I would like to thank everyone who participated. From Michal, who managed to capture footage in seven lecture rooms at once, to Bashy, who helped us with the stress test, to Archos and Schmaker, who did the work on the Vhsky side, and Adam Štrauch, who lent us the machine for the external runner.
If you like what we do and appreciate that someone is making OpenAlt streams and talks available on an open platform without ads and tracking, we would be grateful if you supported us with a contribution to one of OSCloud’s accounts, under which Vhsky.cz runs. PeerTube is a great tool that allows us to operate such a service without having Google’s infrastructure, but it doesn’t run for free either.

Leave a Reply